A Displacements of the reticular lamina RL second harmonic red and fundamental blue as a function of frequency 2f0 bottom axes and f0 top axes at 60-. The reticular lamina contains collagen and elastin and is secreted by connective tissue fibroblasts.
Anchoring fibrils extend from the lamina densa and loop around the type III collagen fibrils serving to attach the basal lamina to the underlying loose connective tissue of the reticular lamina.

Reticular lamina. Reticular lamina n a thin extracellular layer that sometimes lies below the basal lamina is composed chiefly of collagenous fibers and serves to anchor the basal lamina to underlying connective tissue lamina reticularis 1. By measuring sub-nanometer vibrations directly from outer hair cells using a custom-built heterodyne low-coherence interferometer we demonstrate in living gerbil cochleae that the reticular lamina. A layer of the basement membrane.
Within this view the reticular lamina should trade-off between the two conflicting requirements of 1 providing a firm attachment to the outer hair cells and 2. The magnitude and phase differences between reticular lamina and basilar membrane vibrations are absent in postmortem cochleae. The sub-basement membrane is abnormally enlarged and densified.
Laminae or laminas 1. The basal lamina is in turn subdivided into lamina lucida and lamina densa. The expanded area of a leaf or.
The outer hair cell-driven reticular lamina vibration interacts with the basilar membrane traveling wave through the cochlear fluid resulting in maximal vibrations at the best-frequency location consequently enhancing hearing sensitivity. All epithelia rest on a basement membrane which consists of two components the basal lamina secreted by epithelial cells and a reticular lamina secreted by fibroblasts in the underlying connective tissue. The reticular lamina and the basal lamina together constitute the so-called basement membrane a term better avoided.
The reticular lamina showed 40 dB nonlinear compression near the best frequency which is 17 dB greater than that of the basilar membrane 23 dB. Reticular lamina distortion products at different sound levels and f1 frequencies. The denuded epithelium found in asthmatic patients exposes the basement membrane directly to the airspace.
Medical Definition of reticular lamina. Thus highly sensitive. Lamina would be highly responsive to the activity of outer hair cells thus locally enhancing the sensitivity of inner hair cells.
A thin extracellular layer that sometimes lies below the basal lamina is composed chiefly of collagenous fibers and serves to anchor the basal lamina to underlying connective tissue Learn More About reticular lamina Dictionary Entries Near reticular lamina. The phase relation of reticular lamina to basilar membrane vibration changes with frequency by up to 180 degrees from 135 degrees at low frequencies to -45 degrees at the best frequency. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
However the temporal relationship between the outer hair cell-driven reticular lamina vibration and the basilar membrane vibration remains unclear. A thin flat plate or stratum of a composite structure. The real basement membrane in asthma is not abnormal.
Called also layer. Basal lamina lamina basalis the layer of the basement membrane lying next to the basal surface of the adjoining cell layer composed of an electron-dense lamina densa and an electron-lucent lamina. Organ of Cortithe inner sulcus and the reticular lamina.
Home basal lamina and reticular lamina. Reticular lamina f1 phase decreased with frequency magenta lines in Fig. Both the reticular lamina.
The layer of fibrillar extracellular matrix immediately below the basal lamina of epithelial cells. 3g at a rate similar to that of basilar membrane phase response magenta lines in Fig. In the upper turns of the cochlea the margin of the membrane ends in fingerlike projections that.
Phase responses of the reticular lamina are similar to those of the basilar membrane except for a slightly steeper phase slope at frequencies 15 kHz. A thin plate sheet or layer. Reticular lamina synonyms reticular lamina pronunciation reticular lamina translation English dictionary definition of reticular lamina.
The reticular lamina lies beneath the basal lamina and is composed of loose connective tissue with type III collagen fibrils. Its fibrils extend radially and somewhat obliquely to end at its lateral border just above the junction of the reticular lamina and the cells of Hensen. Lamĭ-nah L.
Thickening of the lamina reticularis has been described in asthma even early in the disease process.
 Mucous Membrane Of Stomach The Reddish Gray Mucous Membrane Of The Stomach Composed Of In 2021 Medical Anatomy Medical School Essentials Human Anatomy And Physiology
Mucous Membrane Of Stomach The Reddish Gray Mucous Membrane Of The Stomach Composed Of In 2021 Medical Anatomy Medical School Essentials Human Anatomy And Physiology
 Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Med School Study Anatomy Class
Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Med School Study Anatomy Class
 Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
 Organ Of Corti Neurowissenschaften Wissenschaft
Organ Of Corti Neurowissenschaften Wissenschaft
 Compact Bone Definition Structure Function Facts Cancellous Bone Human Bone Structure Human Bones
Compact Bone Definition Structure Function Facts Cancellous Bone Human Bone Structure Human Bones
 Human Ear Organ Of Corti Ear Anatomy Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
Human Ear Organ Of Corti Ear Anatomy Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
 Pin By Amir Karkhi On Ent Ear Anatomy Middle Ear Anatomy Middle Ear
Pin By Amir Karkhi On Ent Ear Anatomy Middle Ear Anatomy Middle Ear
 Useful Notes On The Epithelial Tissues Of Human Body General Anatomy Basement Membrane Collagen Fibers Tissue
Useful Notes On The Epithelial Tissues Of Human Body General Anatomy Basement Membrane Collagen Fibers Tissue
 Thalamic Reticular Nucleus Part Of The Ventral Dorsal Thalamus Forms A Capsule Around The Thalamus Laterally It Is Neuron Structure Cerebral Cortex Neurons
Thalamic Reticular Nucleus Part Of The Ventral Dorsal Thalamus Forms A Capsule Around The Thalamus Laterally It Is Neuron Structure Cerebral Cortex Neurons
 Pin On Oral Mucosa Part 1 Share
Pin On Oral Mucosa Part 1 Share
 Organ Of Corti Hair Cells Deiters Cell Hensen Claudius Boettcher Note Only Map 2 I E Membrane Asso Study Notes Speech And Language Make Flash Cards
Organ Of Corti Hair Cells Deiters Cell Hensen Claudius Boettcher Note Only Map 2 I E Membrane Asso Study Notes Speech And Language Make Flash Cards
 Thin Skin Integumentary System Human Anatomy And Physiology Histology Slides
Thin Skin Integumentary System Human Anatomy And Physiology Histology Slides
 Basement Membrane Membrane Collagen Fibers
Basement Membrane Membrane Collagen Fibers
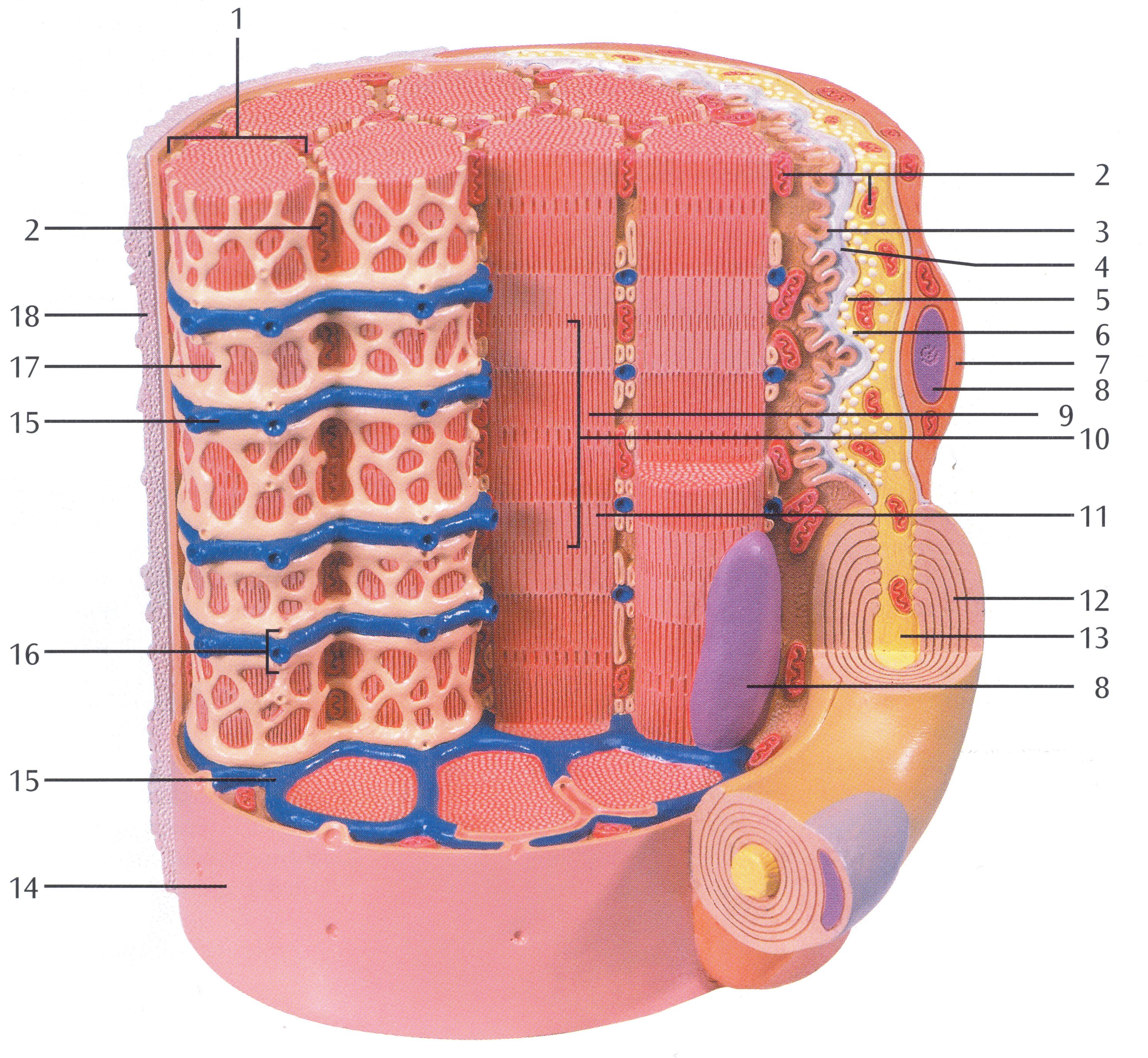 Muscle Fiber 1 Myofibrils 2 Mitochondrium 3 Postsynaptic Membrane 4 Synapti Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical School Studying Neuromuscular Junction
Muscle Fiber 1 Myofibrils 2 Mitochondrium 3 Postsynaptic Membrane 4 Synapti Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical School Studying Neuromuscular Junction
 Organ Of Corti On Basilar Membrane Pillar Cells Rods Of Corti Reticular Lamina Nerve Fiber Membrane Cell
Organ Of Corti On Basilar Membrane Pillar Cells Rods Of Corti Reticular Lamina Nerve Fiber Membrane Cell





0 Comments