Acts as a filter between epithelium and underlying CT. The basement membrane BM is a 50- to 100-nm layer of speci alized extracellular matrix ECM protein complex found basolateral to all cell monolayers epithelium and endothelium in the body.
 Schematic Diagram Of Typical Components Found In Basement Membranes Download Scientific Diagram
Schematic Diagram Of Typical Components Found In Basement Membranes Download Scientific Diagram
Skin Basement Membrane The Foundation Of Epidermal Integrity Bm Functions And Diverse Roles Bridging Molecules Nidogen Perlecan.

Basement membrane function. Non-cellular protein and polysaccharide rich layer. Basement membranes BMs are present in every tissue of the human body. This is achieved by cell-matrix adhesions through cell adhesion molecules CAMs.
All epithelium and endothelium is in direct association with BMs. BMs are a composite of several large glycoproteins and form an organized scaffold to provide structural support to the tissue and also offer functional input to modulate cellular function. The basement membrane also provides a barrier between the tissue that lines the surface of organs and the internal tissues.
The primary function of the basement membrane is to anchor down the epithelium to its loose connective tissue underneath. Cells migrate along basement membranes during development basement membranes are required for the polarization of cells in both the embryo and the adult and basement membranes serve as substrates for cell adhesion and. In most epithelia the basement membrane prevents penetration from the underlying lamina propria into the epithelium.
The basement membrane acts as a mechanical barrier preventing malignant cells from invading the deeper tissues. Function and Importance The primary function of the basement membrane is to anchor down the epithelium to its loose connective tissue underneath. Basement membrane the is tissue sculpting by fibrils sciencedirect basement membranes in the cornea and other ans that monly develop fibrosis springerlink basement membrane regulates fibronectin anization using sliding focal adhesions driven by a contractile winch sciencedirect cell membrane location surrounding the.
The basement membrane or basal lamina is a sheet of proteins and other substances to which epithelial cells adhere and that forms a barrier between tissues. The importance of basement membranes in development and adult tissue function has been inferred from a number of observations. Basement membrane has three main functions.
Basement membranes are a pathway for migrating cells during development and repair processes eg healing of skin wounds. Epithelial tissue lines parts of the body that are. The Glomerular Basement Membrane As A Barrier To Alin Nature Reviews Nephrology.
For example in the skin the basement membrane keeps the layers of the skin attached to one another. Molecular filtering -epithelial cells require a basement membrane as a structural support. In the kidney the basement membrane of the renal.
This is achieved by cell-matrix adhesions through substrate adhesion molecules SAMs. The basement membrane BM is a specialized class of ECM proteins. Scaffold for growth differentiation and migration of cells during embryonic growth.
The basement membrane has a role in compartmentation within organisms regulation of cell migration by acting as a barrier provision of mechanical support and acts as a reservoir of GROWTH FACTORS ENZYMES and PLASMA PROTEINS. The main functions of basement membrane are cell adhesion diffusion barrier and regulation of cell growth. However the basement membranes main function is to anchor the epithelium to the connective tissue underneath.
Once tumours are able to break through this membrane cancerous cells not only invade surrounding tissue substances. The glomerular basement membrane is a trilaminar membrane consisting of the lamina densa in the middle lamina interna next to the endothelial cells and lamina externa next to the podocytes. The podocytes and endothelial cells secrete proteins to make up the basement membrane.
The term for basal lamina often includes the reticular lamina and is often used interchangeably with basement membrane. So far the role of the BM has remained underinvestigated in IPAH. The basement membrane also provides a protective barrier against foreign objects and malignant cells.
Basement Membrane Structure And Function. In pulmonary arteries the BM is in close contact and direct proximity to vascular cells including endothelial cells.
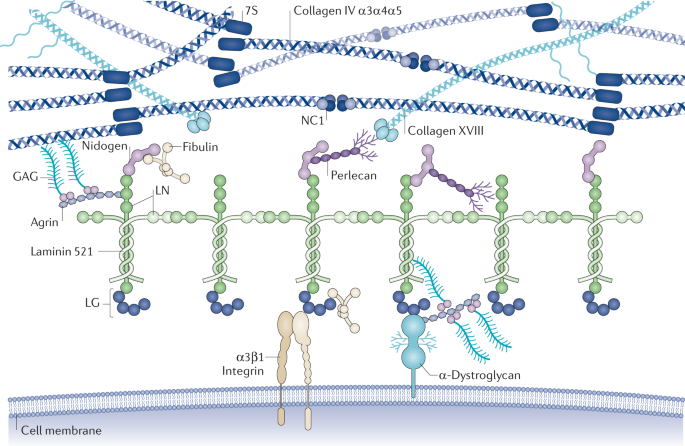 Complexities Of The Glomerular Basement Membrane Nature Reviews Nephrology
Complexities Of The Glomerular Basement Membrane Nature Reviews Nephrology
 The Biology Of The Basement Membrane Plastic Surgery Key
The Biology Of The Basement Membrane Plastic Surgery Key
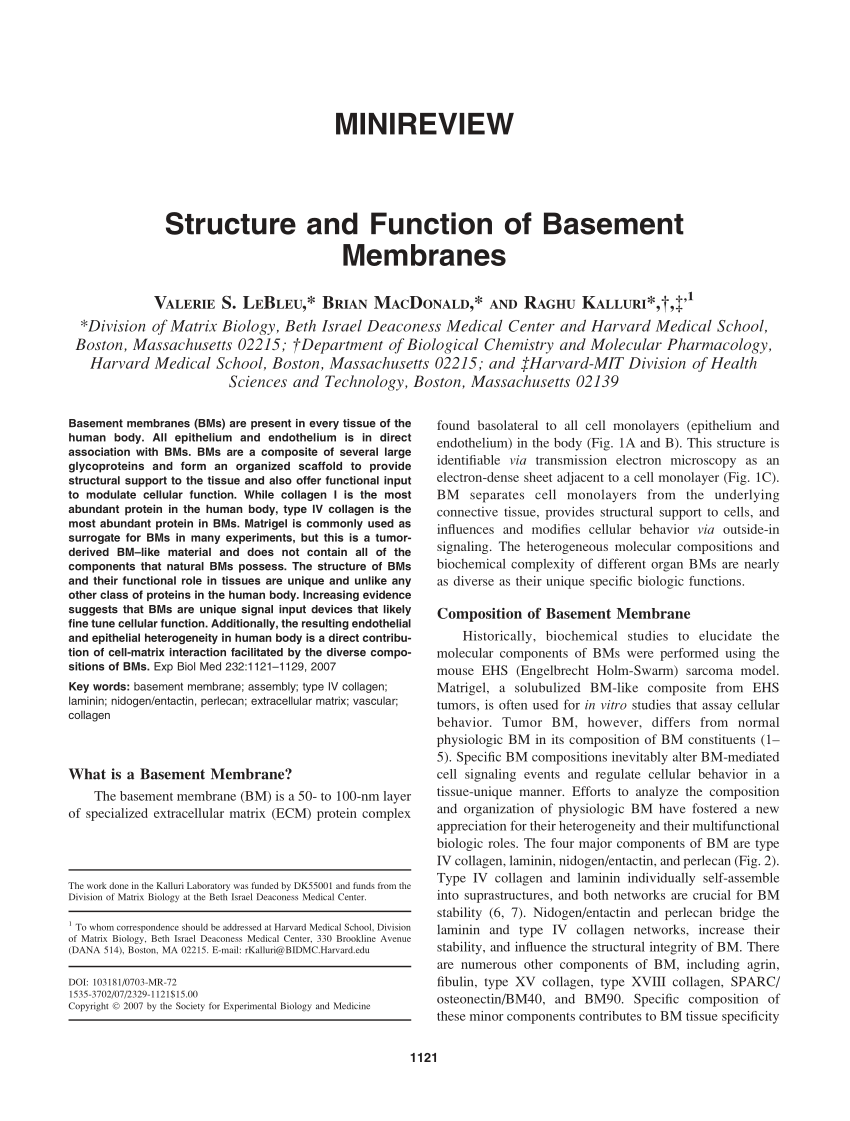 Pdf Structure And Function Of Basement Membranes
Pdf Structure And Function Of Basement Membranes
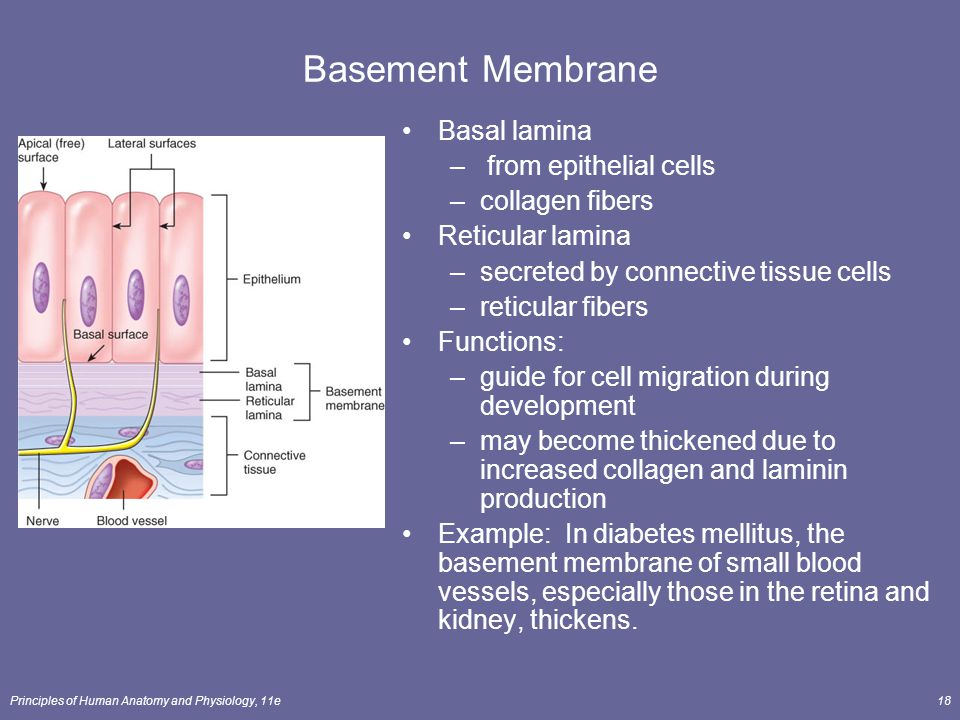 What Is The Basal Lamina And Basement Membrane
What Is The Basal Lamina And Basement Membrane
 Schematic Drawing Of The Molecular Structure Of A Basement Membrane Download Scientific Diagram
Schematic Drawing Of The Molecular Structure Of A Basement Membrane Download Scientific Diagram
 Basement Membrane Basement Membrane The Basement Membrane Is
Basement Membrane Basement Membrane The Basement Membrane Is
 The Biology Of The Basement Membrane Plastic Surgery Key
The Biology Of The Basement Membrane Plastic Surgery Key
 Glomerular Basement Membrane Wikiwand
Glomerular Basement Membrane Wikiwand
 Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Basement Membrane Assignment Point
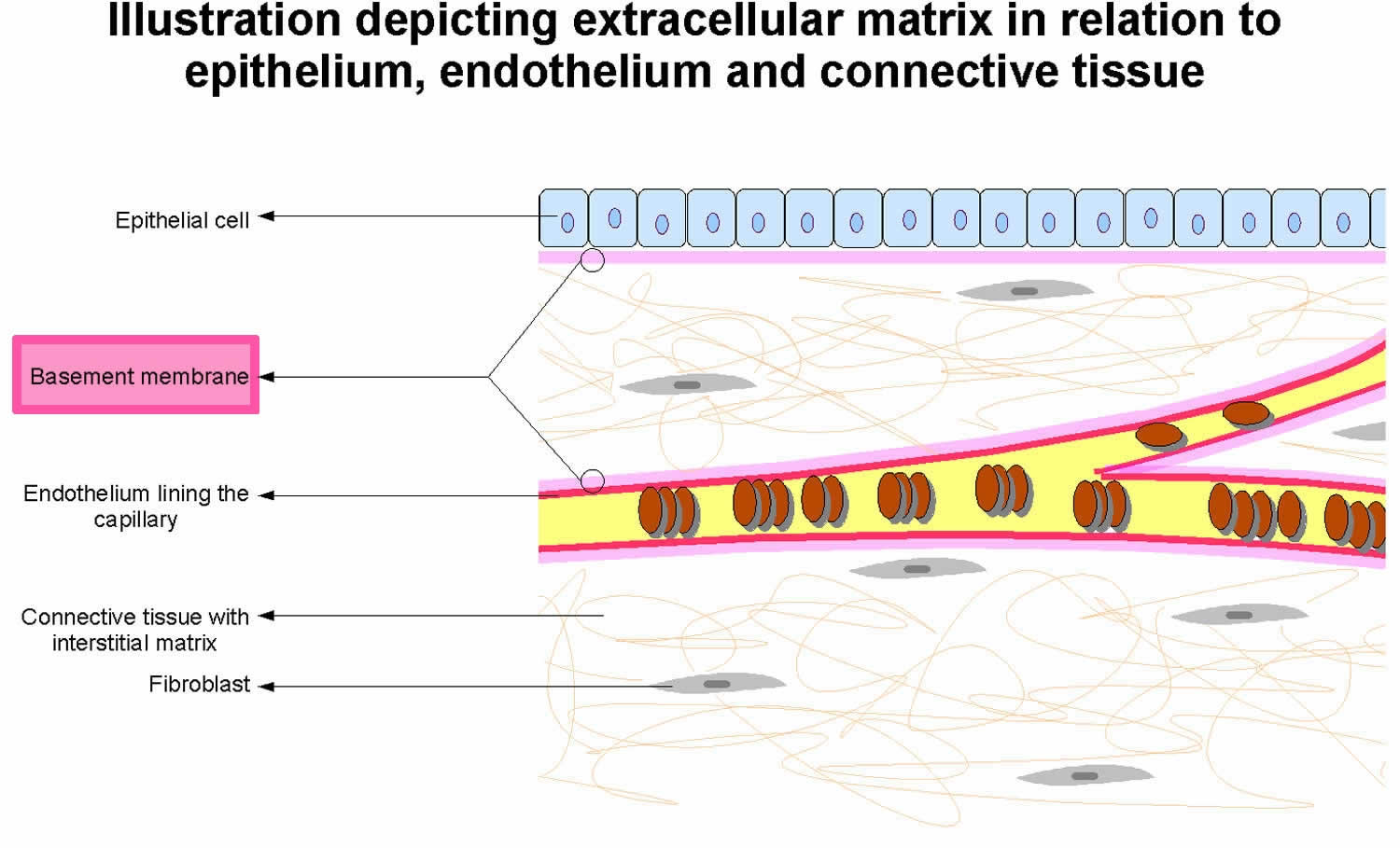 Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Structure And Function
Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Structure And Function
 Corneal Epithelial Basement Membrane Structure Function And Regeneration Sciencedirect
Corneal Epithelial Basement Membrane Structure Function And Regeneration Sciencedirect
 Basement Membranes In Development And Disease Abstract Europe Pmc
Basement Membranes In Development And Disease Abstract Europe Pmc
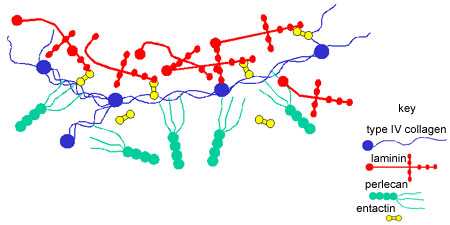 Connective Tissue The Histology Guide
Connective Tissue The Histology Guide
 Representative Diagram Of The Epidermis The Basement Membrane Download Scientific Diagram
Representative Diagram Of The Epidermis The Basement Membrane Download Scientific Diagram
 Basement Membranes Current Biology
Basement Membranes Current Biology
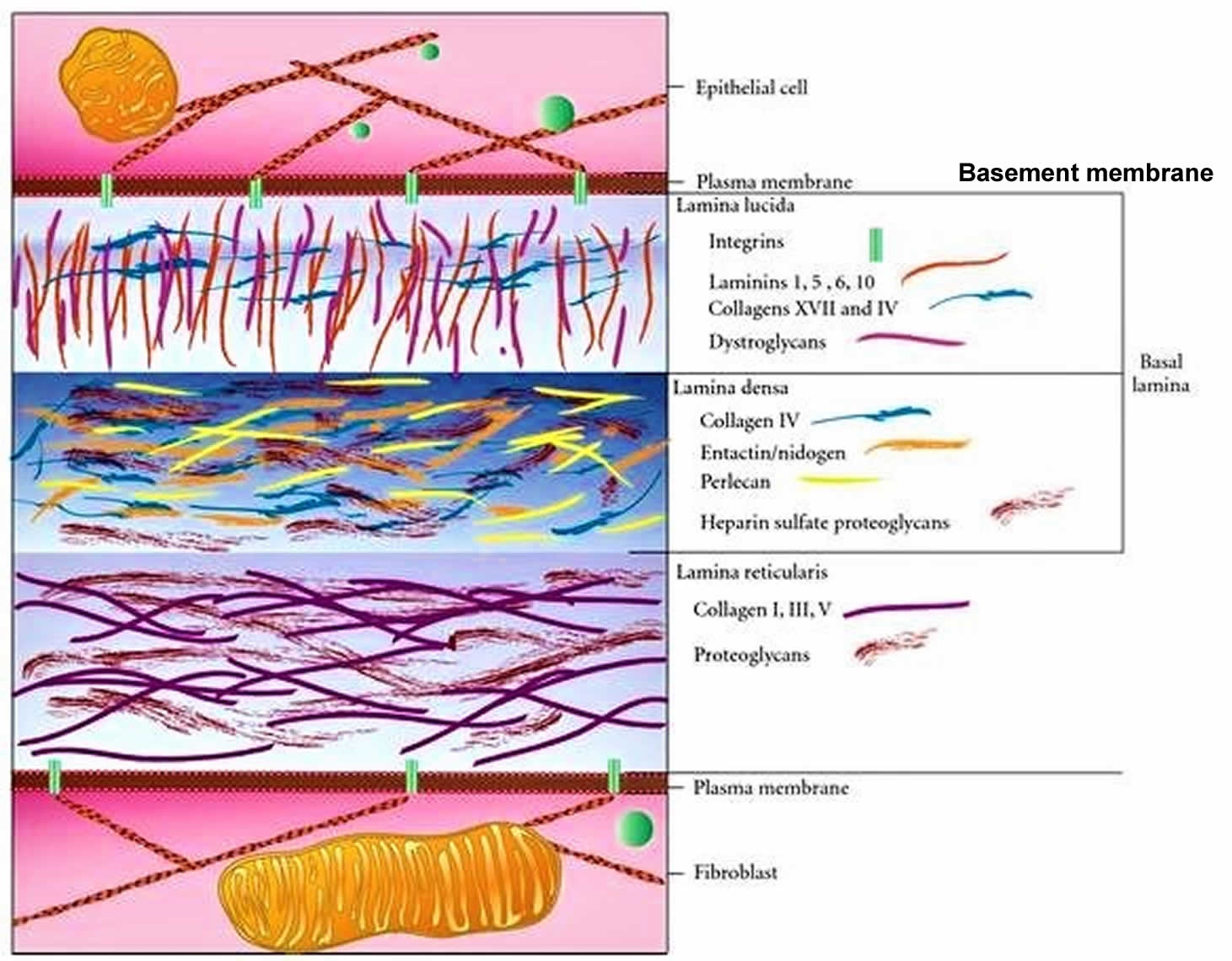 Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Structure And Function
Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Structure And Function
 Histology Study Of Cells Tissues And Organs As
Histology Study Of Cells Tissues And Organs As
 Basement Membrane The Basement Membrane Underlies The Typical Cellular Download Scientific Diagram
Basement Membrane The Basement Membrane Underlies The Typical Cellular Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments