A thin delicate membrane of protein fibres and mucopolysaccharides separating an epithelium from underlying tissue. Basement membrane definition anatomy.
 Glomerular Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Glomerular Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Basement Membrane Definition thin acellular structure always located between any form of epithelium and its underlying connective tissue Parts of Basement Membrane.
Basement membrane definition anatomy. -Nourishment through basement membrane-Many Layers-Most active viable cells are close to basement membrane-Dead cells are farther away from basement membrane. Basement Membrane Anatomy Britannica. Basement membrane a sheet of amorphous extracellular material upon which the basal surfaces of epithelial cells rest.
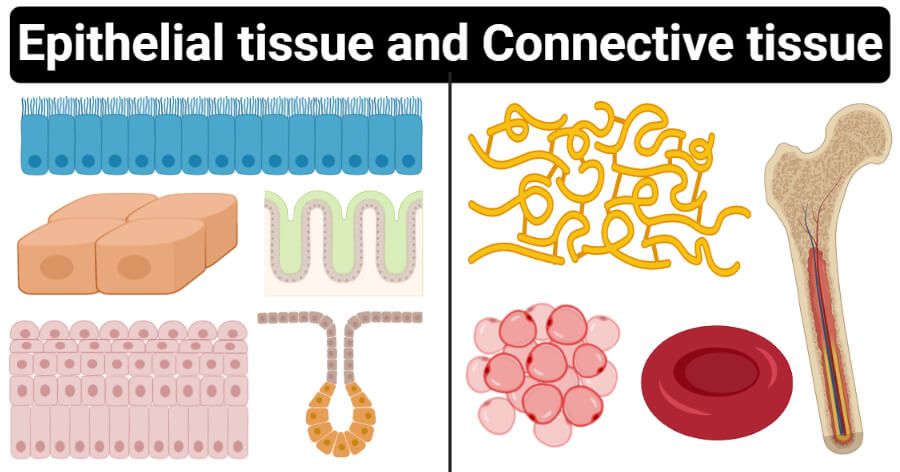
Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology I. A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body skin organs pericardium internal passageways that open to the exterior of the body mucosa of stomach and the lining of the moveable joint cavities. Basement-membrane meaning A thin delicate layer of connective tissue underlying the epithelium of many organs.
It is also associated with muscle cells Schwann cells fat cells and capillaries interposed between the cellular elements and the underlying connective tissue. Basement Membrane Causes Symptoms Treatment Basement Membrane. Epidermis of the skin.
There are two basic types of tissue membranes. The turning points are called mesangial angles. Basement membranes are thin sheet-like extracellular structures that form an anatomical barrier wherever cells meet connective tissues.
At the border between both parts the GBM changes from a convex pericapillary into a concave perimesangial course. Topographically the GBM consists of a peripheral pericapillary and a perimesangial part. The basement membrane lies between the epidermis or outer layer of skin and the dermis the middle layer of skin keeping them tightly connected.
A thin delicate membrane of protein fibers and glycosaminoglycans separating an epithelium from underlying tissue. Structure and function of basement membranes. Not even the effects of gravity can destroy this anchoring system.
The basal surface of most epithelial tissues is attached to a basement membrane which is specialized type of extracellular material secreted by the epithelial. Between the basal surface of epithelial cells and the underlying connective tissue is the basement membrane which varies markedly from place to place and in certain disease states. BMs are a composite of several large glycoproteins and form an organized scaffold to provide structural support to the tissue and also offer functional input to m.
The basement membrane lies between the epidermis and the dermis keeping the outside layer tightly connected to the inside layer. A thin membranous layer of connective tissue that separates a layer of epithelial cells from the underlying lamina propia. Adipose Tissue And Loose Connective Tissue Functions And.
Between the basal surface of epithelial cells and the underlying connective tissue is the basement membrane which varies markedly from place to place and in certain disease states. All epithelium and endothelium is in direct association with BMs. Basement membranes BMs are present in every tissue of the human body.
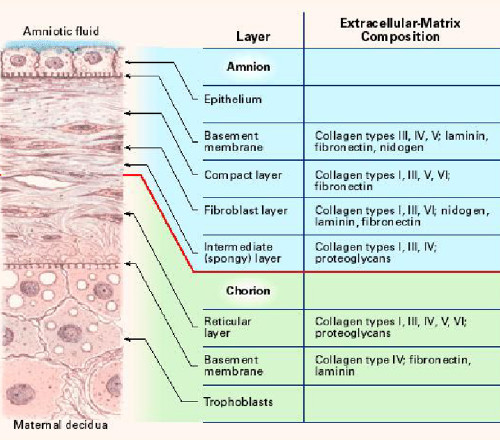
They provide a substrate for organs and cells and relay important signals for the development of organs and for differentiation and maintenance of the tissue. The basement membrane or basal lamina is a sheet of proteins and other substances to which epithelial cells adhere and that forms a barrier between tissues. Connective tissue and epithelial membranes Figure 414.
Definition of basement membrane. Once tumours are able to break through this membrane cancerous cells not only invade surrounding tissue substances. Nearby tissues by breaching the basement membrane.
The glomerular basement membrane represents the skeletal backbone of the glomerular tuft. You have a single layer of cells attached to a membrane of connective tissue called the basement membrane.
 Chapter 1 Building Blocks Of Anatomy Organs Tissues And Systems Flashcards Quizlet
Chapter 1 Building Blocks Of Anatomy Organs Tissues And Systems Flashcards Quizlet
 Pdf Basement Membranes In The Cornea And Other Organs That Commonly Develop Fibrosis
Pdf Basement Membranes In The Cornea And Other Organs That Commonly Develop Fibrosis
 The Anatomy Of The Skin The Skin Consists Of Three Layers Fat Dermis Download Scientific Diagram
The Anatomy Of The Skin The Skin Consists Of Three Layers Fat Dermis Download Scientific Diagram
 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue Types Body Tissues Tissue
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue Types Body Tissues Tissue
 Corneal Anatomy Physiology And Wound Healing Ento Key
Corneal Anatomy Physiology And Wound Healing Ento Key
 Principles Of Human Anatomy And Physiology 11e1 Chapter 4 The Tissue Level Of Organization Lecture Outline Ppt Download
Principles Of Human Anatomy And Physiology 11e1 Chapter 4 The Tissue Level Of Organization Lecture Outline Ppt Download
 Pin By Justin Taphorn On Epithelial Tissue Basement Membrane Exocrine Gland Membrane
Pin By Justin Taphorn On Epithelial Tissue Basement Membrane Exocrine Gland Membrane
 The Dermal Lamella Is Distinct From The Basement Membrane And Is Download Scientific Diagram
The Dermal Lamella Is Distinct From The Basement Membrane And Is Download Scientific Diagram
Basement Membrane Definition Anatomy
 Basement Membrane Definition Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram
Basement Membrane Definition Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram
 15 Differences Between Epithelial Tissue And Connective Tissue Tissue Tissue Types Basement Membrane
15 Differences Between Epithelial Tissue And Connective Tissue Tissue Tissue Types Basement Membrane
 Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Med School Study Anatomy Class
Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Med School Study Anatomy Class
 Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Basement Membrane An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 The Basement Membrane Is Found Between A Epithelium And Connective Tissue B Epithelium And Extracellular Material C Epithelium And Intracellular Material D Extracellular Material And Intracellular Material E Interstitial Fluid And
The Basement Membrane Is Found Between A Epithelium And Connective Tissue B Epithelium And Extracellular Material C Epithelium And Intracellular Material D Extracellular Material And Intracellular Material E Interstitial Fluid And
 Stratified Squamous Epithelium Definition And Function Biology Dictionary Squamous Stratified Squamous Epithelium Basement Membrane
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Definition And Function Biology Dictionary Squamous Stratified Squamous Epithelium Basement Membrane
 Pin By Justin Taphorn On Epithelial Tissue Tissue Biology Human Anatomy And Physiology Cells Project
Pin By Justin Taphorn On Epithelial Tissue Tissue Biology Human Anatomy And Physiology Cells Project
 Capillary The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Capillary The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
 Basement Membrane Epidermis Google Search Kosmetologiya Uroki Biologii Biologiya
Basement Membrane Epidermis Google Search Kosmetologiya Uroki Biologii Biologiya
 Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
0 Comments