Within this view the reticular lamina should trade-off between the two conflicting requirements of 1 providing a firm attachment to the outer hair cells and 2. The reticular lamina lies beneath the basal lamina and is composed of loose connective tissue with type III collagen fibrils.
 Tight Junctions Tight Junction Cell Junction Gap Junction
Tight Junctions Tight Junction Cell Junction Gap Junction
The reticular lamina is usually thicker than the basal lamina.

Basal lamina and reticular lamina. La lámina basal es esencialmente un retículo laminar de colágeno tipo IV unido a moléculas específicas que le permiten asociarse a las células vecinas yo a la matriz extracelular. The reticular lamina contains collagen and elastin and is secreted by connective tissue fibroblasts. The basal lamina attaches to a reticular lamina which is secreted by the underlying connective tissue.
The internal layer also called basal lamina that directly binds the myofiber sarcolemma and the external layer or fibrillary reticular lamina. Basal lamina lamina basalis the layer of the basement membrane lying next to the basal surface of the adjoining cell layer composed of an electron-dense lamina densa and an electron-lucent lamina. Squamous columnar and cuboidal.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Lâmina reticular composta de colágeno tipo III fibras reticulares que se dispõem igualmente como um tapete molecular aderido à lâmina densa da lâmina basal e ancorada ao tecido conjuntivo por. Reticular lamina is fromed by reticular fibers as the name suggests.
The exact composition of the basal lamina varies between different types of cell. Basement membrane is a thin extracellular layer that commonly consists of two layers the basal lamina lamina densa and reticular lamina. Fibrils from lamina densa anchor the basal lamina to the reticular lamina.
Home basal lamina and reticular lamina. The thin extracellular layer consisting of the basal and reticular lamina that anchors epithelial cells to underlying connective tissue is called the. Called also layer.
The basal lamina lamina thin layer about 3070 nanometers in thickness is closer toand secreted bythe epithelial cells. For instance no blood vessels cross the basement membrane to enter the tissue and. The basal lamina of skeletal muscle cells contains acetylcholinesterase which is an.
Junqueira basic histology page 75. The basal lamina and reticular lamina form the basement membranewhich helps hold it all together. The basal lamina is comprised of the lucida and densa layers while the BM is comprised of the basal lamina and the reticular fibers lamina reticularis below it.
The layer of fibrillar extracellular matrix immediately below the basal lamina of epithelial cells. The basal lamina is in turn subdivided into the lamina lucida and the lamina densa. Lamĭ-nah L.
The reticular lamina and the basal lamina together constitute the so-called basement membrane a term better avoided. In the kidney the basal lamina acts as a molecular filterAt the neuromuscular junction the basal lamina that surrounds the muscle cells separates the nerve cell from the muscle cell at the synapse and helps to regenerate the synapse after injury and helps to localise acetylcholine receptors. The basement membrane is subdivided in two layers.
Some facts on the basement membrane. The main components of basal lamina are type 4 collagen the glycoproteins laminin and entacin and proteoglycans. The OHCs are supported at their upper poles by the reticular lamina and at their bottom ends by the supporting cells of the organ of Corti.
Leaving aside for the moment the question of whether there is a strong bond between the hair cells and their supporting cells it is clear that contraction of the basal part of the OHCs will produce a force pulling the BM and the reticular lamina closer. Lamina would be highly responsive to the activity of outer hair cells thus locally enhancing the sensitivity of inner hair cells. Epithelial tissues are nearly completely avascular.
The basal lamina is composed of a lamina lucida and a lamina densa which rests in turn on the reticular lamina of the dermis. A thin flat plate or stratum of a composite structure. 46 While the fibrils of the reticular lamina are collagenous and embedded in an amorphous proteoglycan-rich ground substance the basal lamina.
Asked Sep 19 2015 in Anatomy Physiology by Kayla. The difference between a basal lamina and a basement membrane is that a the basal lamina is thicker. The basal lamina together with the reticular lamina.
 Fabrication Enterprises 12 4559 Anatomical Model Microanatomy Muscle Fiber 10 000 Times Magnified In 2021 Anatomy Models Skeletal Muscle Medical Research
Fabrication Enterprises 12 4559 Anatomical Model Microanatomy Muscle Fiber 10 000 Times Magnified In 2021 Anatomy Models Skeletal Muscle Medical Research
 Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands Anatomy And Physiology Medicine Notes Biology Classroom
Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands Anatomy And Physiology Medicine Notes Biology Classroom
 Basement Membrane Membrane Collagen Fibers
Basement Membrane Membrane Collagen Fibers
 Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Med School Study Anatomy Class
Basement Membrane Basement Membrane Med School Study Anatomy Class
 Human Physiology Muscle Physiology Medical School Essentials Nursing School Studying
Human Physiology Muscle Physiology Medical School Essentials Nursing School Studying
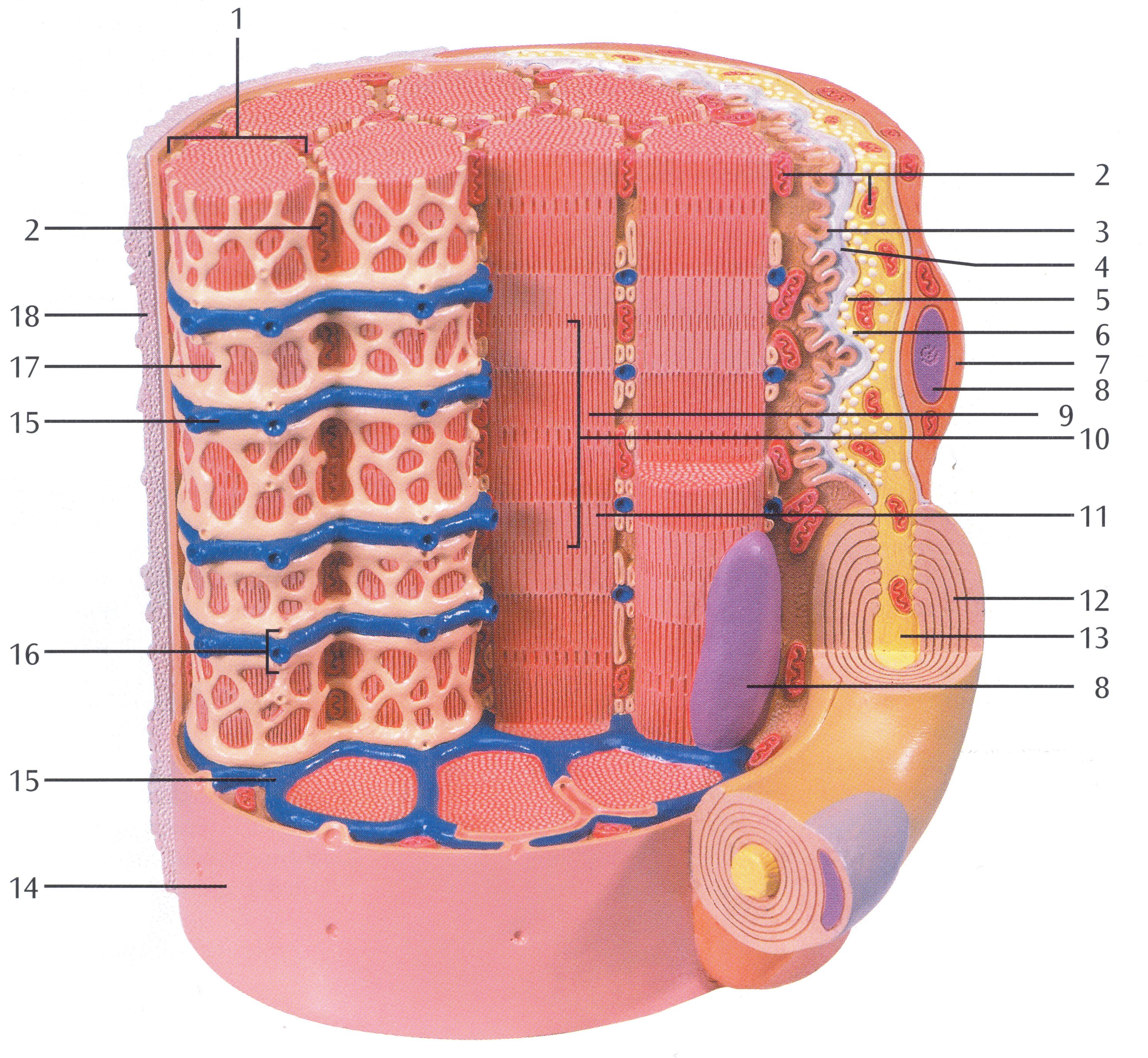 Muscle Fiber 1 Myofibrils 2 Mitochondrium 3 Postsynaptic Membrane 4 Synapti Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical School Studying Neuromuscular Junction
Muscle Fiber 1 Myofibrils 2 Mitochondrium 3 Postsynaptic Membrane 4 Synapti Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical School Studying Neuromuscular Junction
 Pin On Oral Mucosa Part 1 Share
Pin On Oral Mucosa Part 1 Share
 Pin By Amir Karkhi On Ent Ear Anatomy Middle Ear Anatomy Middle Ear
Pin By Amir Karkhi On Ent Ear Anatomy Middle Ear Anatomy Middle Ear
 Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
 48 Ideas For Skin Model Labeled Human Anatomy And Physiology Skin Model Anatomy And Physiology
48 Ideas For Skin Model Labeled Human Anatomy And Physiology Skin Model Anatomy And Physiology
 Collagen Types And Locations Collagen Lymphatic System Dermis
Collagen Types And Locations Collagen Lymphatic System Dermis
 Basic Histology Quiz Histology Slides Quiz Neon Signs
Basic Histology Quiz Histology Slides Quiz Neon Signs
 Organ Of Corti On Basilar Membrane Pillar Cells Rods Of Corti Reticular Lamina Nerve Fiber Membrane Cell
Organ Of Corti On Basilar Membrane Pillar Cells Rods Of Corti Reticular Lamina Nerve Fiber Membrane Cell
 Compact Bone Definition Structure Function Facts Cancellous Bone Human Bone Structure Human Bones
Compact Bone Definition Structure Function Facts Cancellous Bone Human Bone Structure Human Bones
 Simple Columnar Epithelium Introduction Types Functions Basement Membrane Tissue Types Exocrine Gland
Simple Columnar Epithelium Introduction Types Functions Basement Membrane Tissue Types Exocrine Gland
 Transitional Unstretched Specialized My Favorite B C It Was The Easiest To Identify Of The Epithelial Histologia
Transitional Unstretched Specialized My Favorite B C It Was The Easiest To Identify Of The Epithelial Histologia



0 Comments