Parts of Basement Membrane. Basement membrane definition is a thin membranous layer of connective tissue that separates a layer of epithelial cells from the underlying lamina propia.
 Basement Membrane Squamous Cell Basal Cell
Basement Membrane Squamous Cell Basal Cell
The basement membrane is a structure that supports overlying epithelial or endothelial cells.

Basement membrane definition. The basement membrane or basal lamina is a sheet of proteins and other substances to which epithelial cells adhere and that forms a barrier. Basement membranes BMs are thin sheets of specialized extracellular matrix that were first identified by transmission electron microscopy as continuous ribbon-like structures adjacent to a subset of cells. Thin acellular structure always located between any form of epithelium and its underlying connective tissue.
Basement membrane definition a thin extracellular membrane underlying epithelial tissue. The basement membrane that is located in the kidneys specifically filters out smaller molecules while retaining large molecules such as proteins within the cells. But basement membranes arent just found in the.
The basement membrane lies between the epidermis and the dermis keeping the outside layer tightly connected to the inside layer. Both compartments are connected by the basement membrane BM composed of a set of distinct glycoproteins and proteoglycans. All epithelium and endothelium is in direct association with BMs.
Structure and function of basement membranes. A thin delicate membrane of protein fibres and mucopolysaccharides separating an epithelium from underlying tissue. The epidermis functions in skin as first defense line or barrier against environmental impacts resting on extracellular matrix ECM of the dermis underneath.
Basal lamina Reticular lamina deep layer Connective Tissue Nerves and blood vessels. Basement membrane is a thin extracellular layer that commonly consists of two layers the basal lamina lamina densa and reticular lamina. They are evolutionarily ancient structures being present even in primitive organisms such as sponges and HydraIn mammals BMs underlie endothelial and epithelial cells and surround all.
Composed of three successive layers lamina lucida lamina densa and lamina fibroreticularis a matrix of collagen. The basement membrane located on the interior of a blood vessel is involved in the process of angiogenesis. The basement membrane or basal lamina is a sheet of proteins and other substances to which epithelial cells adhere and that forms a barrier between tissues.
Not even the effects of gravity can destroy this anchoring system. Angiogenesis is the development of new blood vessels and this occurs. A thin extracellular supporting layer that separates a layer of epithelial cells from the underlying lamina propria and is composed of the basal lamina and reticular lamina.
Between the basal surface of epithelial cells and the underlying connective tissue is the basement membrane which varies markedly from place to place and in certain disease states. Medical Definition of basement membrane 1. The GBM is one of the thickest basement membranes in the body.
Epithelium is a type of tissue that forms glands and lines the inner and outer surfaces of organs and structures throughout the body. BMs are a composite of several large glycoproteins and form an organized scaffold to provide structural support to the tissue and also offer functional input to m. Basement membranes BMs are present in every tissue of the human body.
Herein we are reviewing molecular aspects of BM structure composition and function regarding not only i. The basement membrane membrana basalis is a thin layer of basal lamina and reticular lamina that anchors and supports the epithelium and endothelium. Once tumours are able to break through this membrane cancerous cells not only invade surrounding tissue substances.
Bāsmĕnt membrān An amorphous extracellular layer closely applied to the basal surface of epithelium and also investing muscle cells fat cells and Schwann cells. The GBM is a specialized structure that envelops the peripheral capillary loops and the paramesangial areas and is continuous with the basement membrane of Bowmans capsule at the vascular pole of the glomerulus.
 5 1 Characteristics Of Epithelia Basement Membrane Basement Home Improvement Projects
5 1 Characteristics Of Epithelia Basement Membrane Basement Home Improvement Projects
 Difference Between Cell Migration And Invasion Study Of Tissues Extracellular Fluid Tissue Types
Difference Between Cell Migration And Invasion Study Of Tissues Extracellular Fluid Tissue Types
 What Is The Difference Between Epithelial And Connective Tissue Epithelial Tissue Is Above The Basement Mem In 2021 Study Of Tissues Basement Membrane Collagen Fibers
What Is The Difference Between Epithelial And Connective Tissue Epithelial Tissue Is Above The Basement Mem In 2021 Study Of Tissues Basement Membrane Collagen Fibers
 Basement Membrane Epidermis Google Search Kosmetologiya Uroki Biologii Biologiya
Basement Membrane Epidermis Google Search Kosmetologiya Uroki Biologii Biologiya
 Basement Membrane Membrane Collagen Fibers
Basement Membrane Membrane Collagen Fibers
 Stratified Squamous Epithelium Definition And Function Biology Dictionary Squamous Stratified Squamous Epithelium Basement Membrane
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Definition And Function Biology Dictionary Squamous Stratified Squamous Epithelium Basement Membrane
 Pin By Justin Taphorn On Epithelial Tissue Basement Membrane Exocrine Gland Membrane
Pin By Justin Taphorn On Epithelial Tissue Basement Membrane Exocrine Gland Membrane
 Stratified Columnar Epithelium Structure Functions Examples Basement Membrane Plant Cell Cell Junction
Stratified Columnar Epithelium Structure Functions Examples Basement Membrane Plant Cell Cell Junction
 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue Types Body Tissues Tissue
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue Types Body Tissues Tissue
 Multicellular Organisms Cell Cell Adhesion Cell Matrix Adhesion The Extracellular Matrix Ecm M Habibi Re Basement Membrane Collagen Fibers Biomedical Science
Multicellular Organisms Cell Cell Adhesion Cell Matrix Adhesion The Extracellular Matrix Ecm M Habibi Re Basement Membrane Collagen Fibers Biomedical Science
 Tunica Basement Membrane Full Size
Tunica Basement Membrane Full Size
 Epithelial Tissue Definition Types Functions Examples Tissue Types Basement Membrane Tissue
Epithelial Tissue Definition Types Functions Examples Tissue Types Basement Membrane Tissue
 Epithelial Tissue Anatomy Physiology Body Tissues Basement Membrane Plasma Membrane
Epithelial Tissue Anatomy Physiology Body Tissues Basement Membrane Plasma Membrane
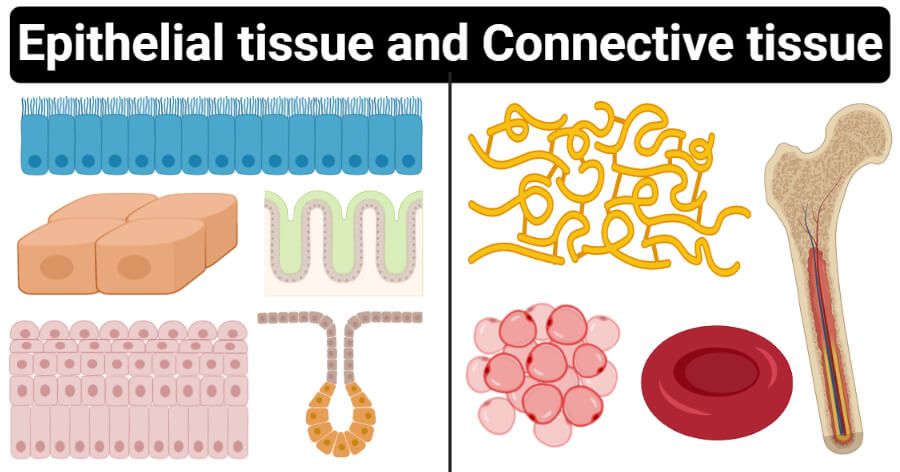 15 Differences Between Epithelial Tissue And Connective Tissue Tissue Tissue Types Basement Membrane
15 Differences Between Epithelial Tissue And Connective Tissue Tissue Tissue Types Basement Membrane
 Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
Special Characteristics Of Epithelia Epithelium Basement Membrane Cell Junction Serous Membrane
 Understanding Squamous Stratified Squamous Epithelium Basement Membrane
Understanding Squamous Stratified Squamous Epithelium Basement Membrane
 Type Of Epithelial Tissue Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar In 2021 Tissue Biology Integumentary System Medical Terms
Type Of Epithelial Tissue Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar In 2021 Tissue Biology Integumentary System Medical Terms


0 Comments